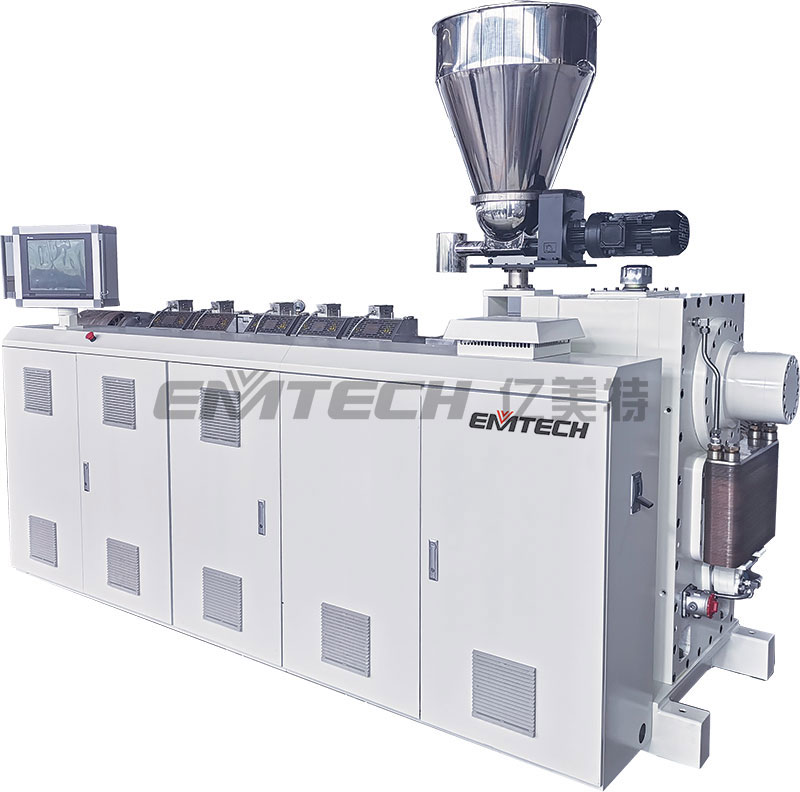
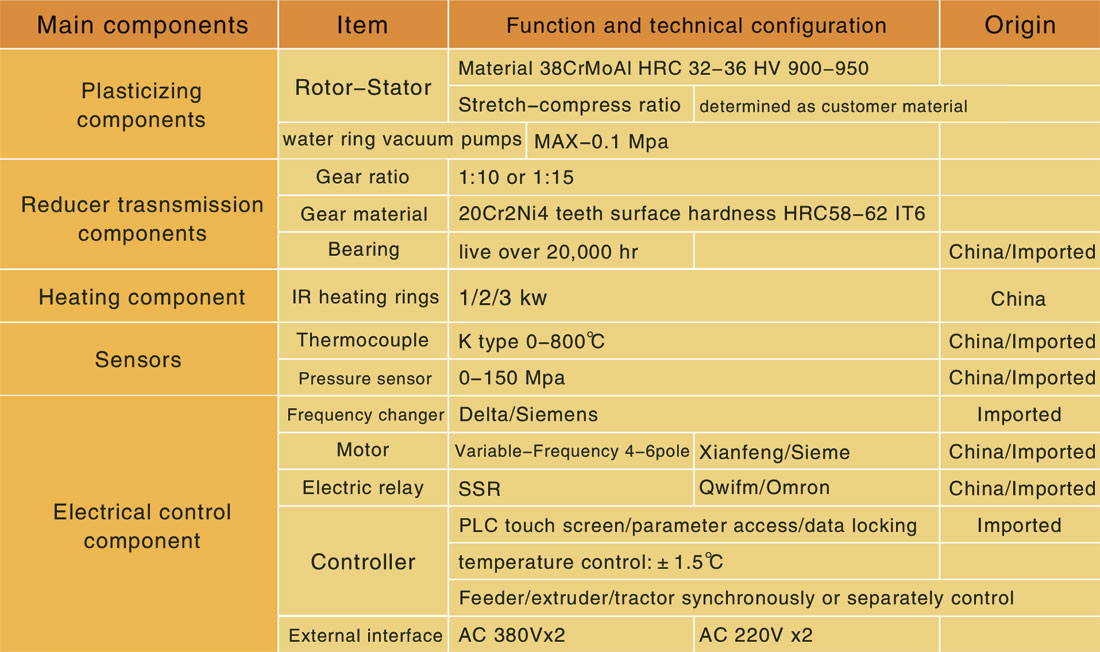
Peristaltic rotating extruder is a new product together developed by EMTECH and South China University of Technology (SCUT) National Engineering Research Center for polymer new-type forming equipment. The extruder is based on the theory of elongation rheology plasticizing transport and related inventions established by Qu Jinping, academician of China Academy of Engineering. Cooperated with relevant R&D teams and investors, EMTECH develops, produces and sells new generation plasticizing extrusion and injection molding equipment, and provides advanced products and related technical services for domestic and international customers
The Principle of Elongation Rheology Plasticizing and Convey
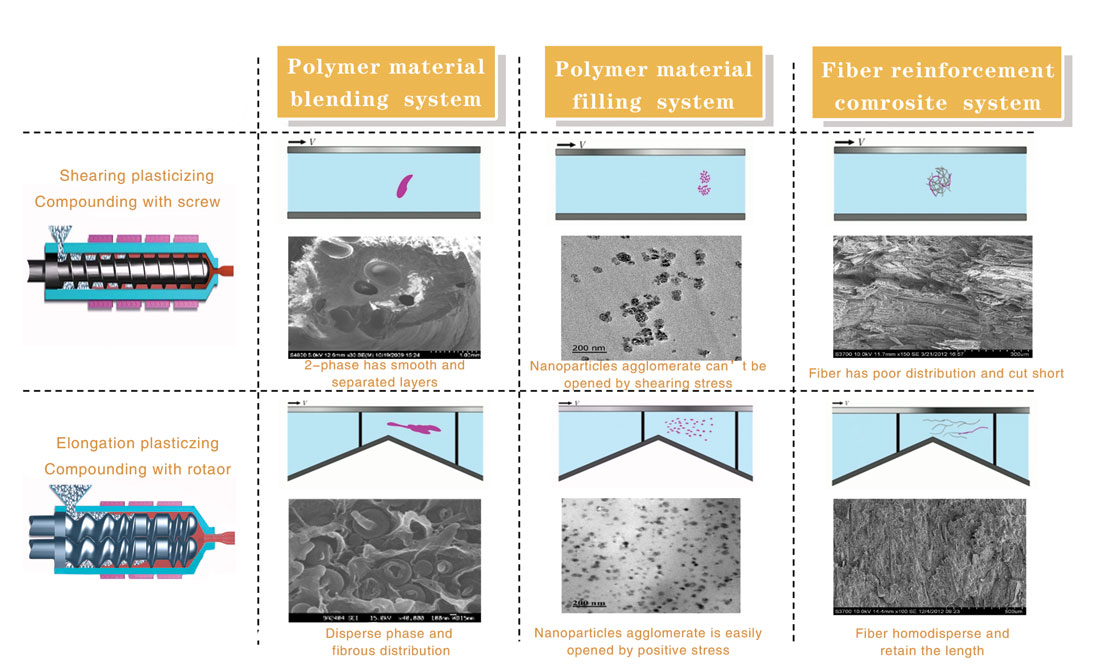
The key technology of Peristaltic Rotating Extruder is utilizing special structured plasticizing part, changing the way of melted flow plasticization and convey from traditional shearing rheology to elongation rheology dominant. The volume of melted flow moves peristaltically during this process. Compared with traditional plasticizing method, elongation rheology causes less damage to molecular chain, hence the material has better uniaxil tensile strength at yield and elongation strain at break. The process needs less heating energy and produce the material with better dispersion. Peristaltic Rotationg Extruder is of great significance in energy saving, resource recycle and improvement of product quality, have huge prospects in world-wide market.
After plastic pellet or powder enters into plasticizing unit, the melted flow ( as figure above) experiences:
Powder/Pallet solid compress
↓
Volume peristalsis alternatively
↓
Homogenization
↓
Volume expansion venting
↓
Repeat peristalsis and Homogenization
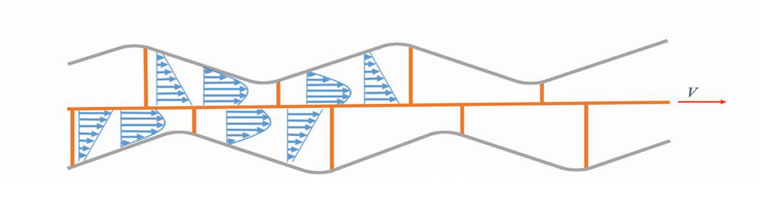
Melted flow experiences multiple extension and compress stages. Whole process is carried out in smooth curved surface, preventing molecular chain from broken and overheat cuased by shearing action. The completion of molecular chain is maximum preserved during this process. The principle is a great breakthrough in polymer processing sector.
Performance Comparison with Traditional Extruder
Pipe type | PVC-M | PVC-U | Traditional Extruder | Peristaltic Extruder | |
Product Standard | CJ/T | ISO | GB/T | ||
Dichloromethane resistance | No erosion is allowed on the surface | No erosion is allowed on the surface | Not inferior to 4N | PASS | PASS |
Tensile yield strength |
| ≥45 |
| ≥42 | ≥45 |
Elongation at break % |
| ≥80 |
| ≥150 | ≥180 |
Drop hammer impact strength | 6.3KG 2m | M 1.0kg 1.6m | M 1.0kg 1.6m | 3.0kg 2m | 6.0kg 2m |
Water pressure testing | 36.0 dn≤63 | 42.0 | 36.0 dn<40 | 38MPa PASS | 42MPa PASS |
Energy consumption ratio |
|
|
| 0.18-0.20 | 0.15-0.18 |
Multiphase composite |
|
|
| Poor dispersion | Uniform dispersion |
※Above date is only for PVC pipe DN110 mm | |||||
Gearbox/Distributor
Main Figures of Gearbox For Parallel Twin-screw Extruder | |||
Type number | ETP 6-51/65 | ETP 6-66/75 | ETP 6-76/90 |
Screw Diameter (mm) | 65 | 75 | 90 |
Center Distance (mm) | 51 | 66 | 76 |
Uniaxial torque (Nm) | 3300 | 5914 | 8700 |
Output speed (rpm) | 60 | 60 | 60 |
Power (kw) | 55 | 75 | 110 |
Uniaxial torque index (Nm/cm³) | 16.3 | 20.6 | 19.9 |
Uniaxial back pressure (kN) | 110 | 150 | 206 |
Overall dimensions (LxWxH mm) | 850x580x1100 | 950x670x1250 | 1100x750x1350 |
Microstructure Comparison Chart
Specifications
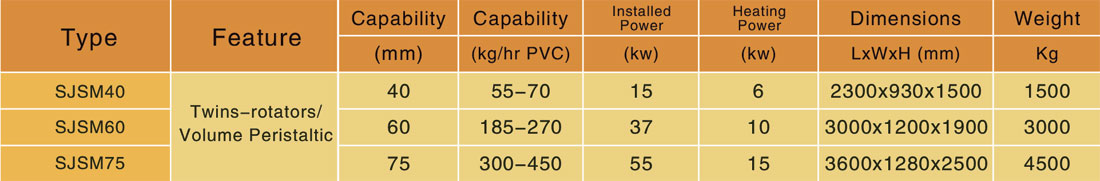
Machine Configuration